enlaces español:
video presentación (Disney) : https://youtu.be/wApZcY3yLkM
video ecosistemas: http://link.edelvives.es/sfpht
que es un ecosistema: https://youtu.be/xypUF5Kr220
https://youtu.be/tPFGdTE_nas
resumen ecosistemas: https://youtu.be/mVMmmg8iOFY
https://youtu.be/QNy5VYZn8yQ
juego: http://link.edelvives.es/uxsbl
video de cadenas alimentarias: http:// link.edelvives.es/uqxrx
ecosistemas terrestres y acuáticos: https://youtu.be/tEAZ2i98HK8, https://youtu.be/FEFFm6O6rHk
amenazas a la biodiversidad: https://youtu.be/upQ1sKe2EU4, https://youtu.be/PRJHetEiAT8
reportaje sobre algunas especies en peligro de extinción: http://link.edelvives.es/tceqn
VIDEO RESUMEN DE ECOSISTEMAS https://youtu.be/vtvByVrt7rI
PROYECTO EN GRUPO:
proyecto de investigación en grupo: http://link.edelvives.es/mwfnf
ENGLISH
BIODIVERSITY
What is biodiversity: It is the wide variety of life on Earth.
All living things need other living things to survive. Plants, humans, animals and micro-organisms depend on each other.
Four reasons why biodiversity is important:
- it provides raw materials for industries such as Wood, meat.
- it is important for scientists to test different microorganisms for medicine.
-it is important for living things as it gives us oxygen to breathe (oxygen comes from plants through photosynthesis)
- It is important for farmers to provide better food and clothing (wool, cotton) .
what is a biodiversity: https://youtu.be/aqtdaIkxnQo
ECOSYSTEMS
Desert, jungle, rainforest, ocean, forest, prairie,pond, Tundra.
https://youtu.be/hIy0ZlyPPDg
https://youtu.be/nYF6CKU8AfM
https://youtu.be/P22epOXwJHg
COMPONENTS OF AN ECOSYSTEM, BIOTIC AND ABIOTIC.
Ecosystem: The living and non-living things in a given geographic area.
Biotic: all living things in an ecosystem: plants, animals, bacteria, fungae
Abiotic: All non-living components of an ecosystem: gases (hydrogen, oxygen,carbon, nitrogen ,phosphorus) , sunlight, water, soil.
https://youtu.be/E1pp_7-yTN4
https://youtu.be/y-wpbhnom70

INTERACTION IN AN ECOSYSTEM
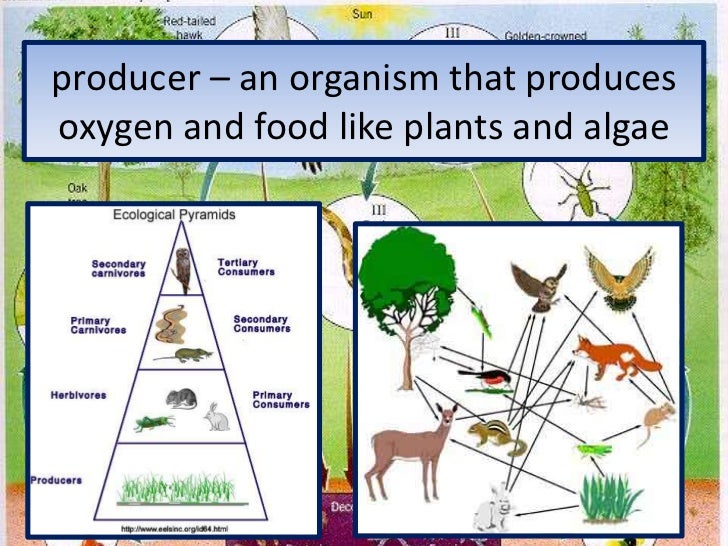
Producers: are plants. Plants take nutrients from the soil and energy from the sun. They carry out photosynthesis to make their own food.
Decomposers: are bacteria and fungi (singular, fungus) that feed off the remains of dead animals and plants. First they break down the nutrients into small pieces.Then, they return these nutrients to the soil, where plants use them.
Consumers: are animals and organisms that eat other living things.
Primary consumers: that eat producers are called herbivores (rabbits eat grass)
Secondary consumers: that eat other consumers are called carnivores (eagles eat rabbits)
tertiary consumers: that eat both producers and other consumers are called omnivores (birds eat fruit and worms)

THE LOSS OF BIODIVERSITY
There are many natural causes of extintion ,however humans are responsable for most of the recent loss of biodiversity in the world.This is a result of several destructive practices and their consequences.
-climate change
-pollution
- hunting and capturing animals
- over exploiting resources
- alteration of hábitats: deforestation,desertification, construction, burning fossil fuels...
- releasing pets into the world.
PROTECTING AND CONSERVING BIODIVERSITY
- National parks and biosphere reserves are created to protect wildlife and its environment
-recycle, reuse, reduce rubbish.
-plant trees
- use public transport or ride a bicycle.
climate change: https://youtu.be/Sv7OHfpIRfU
pollution and prevention: https://youtu.be/tmhiglxga-4
biodiversity loss:
https://youtu.be/DAmJUFDdj4o
extinct animals: https://youtu.be/VrokfZ6mD5A
https://youtu.be/9reZZdKVogA
colourful animals: https://youtu.be/RztMxSB6c6Y
recycle: https://youtu.be/TjnNOCbuoCA
how recycling Works: https://youtu.be/VlRVPum9cp4
ESQUEMA
NATURALES: LOS ECOSISTEMAS
ECOSISTEMA:
es el conjunto formado por un lugar/seres
vivos que habitan en
él. Así como por las relaciones que se establecen en él.
-componente
inerte

Especie población comunidad
Especie: conjunto de organismos con iguales
características que pueden reproducirse
entre ellos (flamenco y garza)
Población:
conjunto de
individuos de la misma especie.(ranas en una charca)
Comunidad:
es el conjunto de poblaciones.
RELACIONES
ENTRE INDIVIDUOS
Depredación: un individuo el depredador se alimenta de su presa.
Parasitismo:
un parásito vive a
costa de un huésped (piojos)
Mutualismo:
es una relación en
la que dos especies se benefician . (garcilla se alimenta de los parásitos del
búfalo y el búfalo se libra de ellos)
Comensalismo: una especie se beneficia de otra
sin perjudicarla (los peces rémora se alimentan de lo que le sobra al tiburón.
ECOSISTEMAS
NATURALES:
Litoral,
charca, bosques,pradera.
ECOSISTEMAS
ARTIFICIALES
Ciudades,cultivos
ECOSISTEMAS
TERRESTRES
Bosque templado,selva,
sabana,desierto
ECOSISTEMA
ACUÁTICO
Agua dulce,
salada, polos.