Enlaces en español (conocimiento cultural)
video del robot Asimo http://link.edelvives.es/ddphs
Isaac Asimov: http:link.edelvives.es/ixmsp
peligros más comunes: http://link.edelvives.es/lblbs
peligros de electrodomésticos sin control: http://link.edelvives.es/tyfwc
tipo de palanca y funcionamiento: http://link.edelvives.es/dlkto
tipos de polea y transmisiones: http://link.edelvives.es/vohxp
video de transmisión: http://link.edelvives.es/ileqh
líneas de fuerza del campo magnético de los imanes: http://link.edelvives.es/xfobh
experiencias de electricidad estática e imanes: http://link.edelvives.es/iwcok
historia de las telecomunicaciones: http://link.edelvives.es/woyup
molino de viento: http://link.edelvives.es/qsxjp
maquinas simples y mapa conceptual: http://link.edelvives.es/wm
RESUMEN UNIDAD 6: LAS
MAQUINAS Y LOS AVANCES TÉCNICOS.
Máquinas simples:
Está formada por una o por varias piezas.
Máquinas compuestas:
Unión de diferentes piezas. Las piezas se agrupan formando partes.
Cada parte se denomina
“operador”
Máquinas simples
palanca, polea, plano inclinado.
Palanca :
F
barra rígida R
-primer género P.A
- segundo género:(cascanueces)
R
F
P.A Nuez
- tercer género: (pinzas para coger hielo)
P.A
R F
polea: formada por una rueda que tiene un canal por el
que pasa una cuerda y un eje sobre el que gira.
Plano inclinado: superficie plana y ángulo.Menor el
ángulo menos fuerza para subir.
Máquinas complejas
:
operadores, engranajes.
Operador mecánico. Transmiten o transforman los
movimientos de unas piezas a otras. Operadores se agrupan y forman
un mecanismo. (manivelas y engranajes)
Operadores
energéticos: acumula energía
para que la máquina funcione. ( pilas, baterías, muelles)
engranajes:
son ruedas dentadas que giran
en torno a un eje.
CIRCUITO
(119)
+ - Motor
M
AVANCES: (122)
ENGLISH: MACHINES
Introduction
-The following inventions changed the world what do you know about them? (investigate with your friend)
plough, printing press, steam engine, typewriter, light bulb, telephone, computer.
Classifying machines
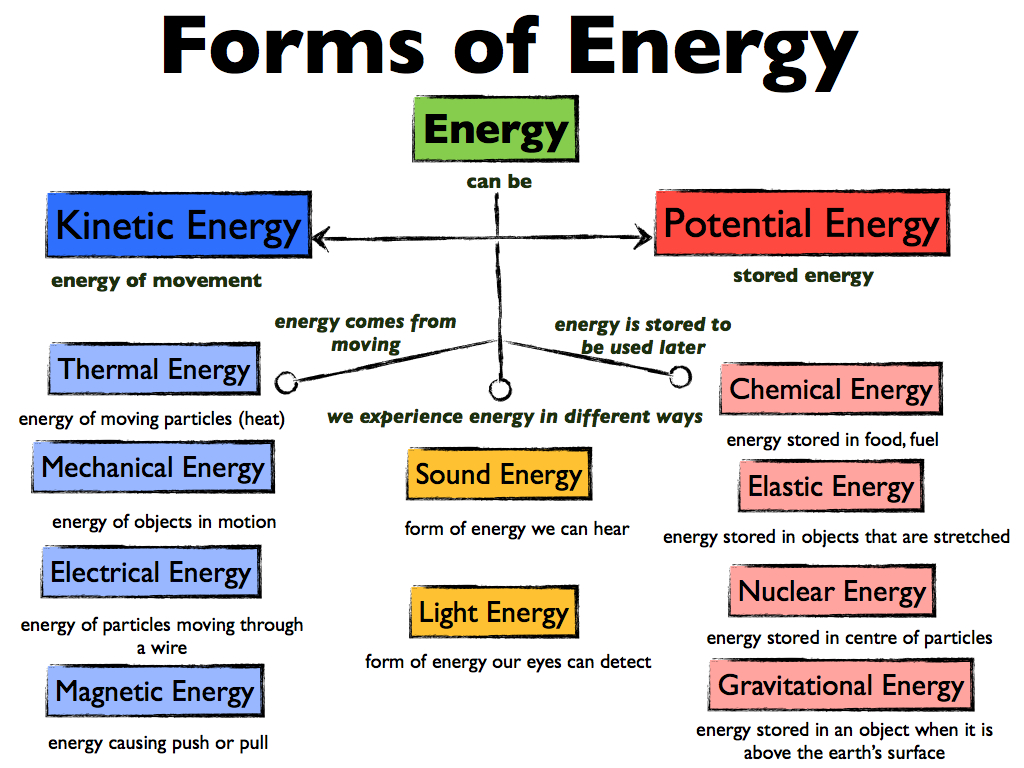
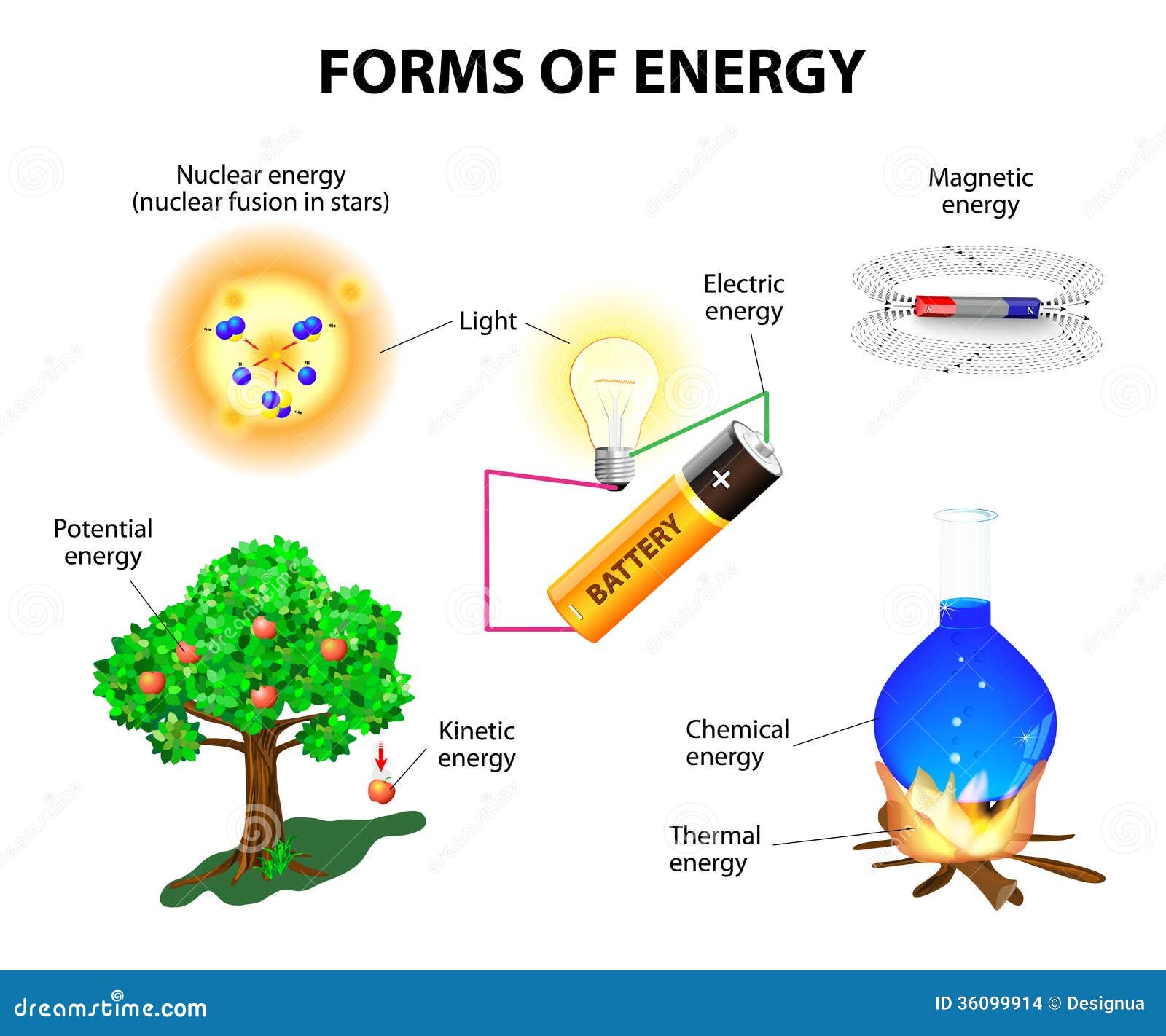
- We can classify machines by the energy source they need to work.
Complete the sentences in your notebook with the words from the list:
1. DVD players need________
2. cars need petrol or___________
3. old mills need wind or ________
4. TV remote controls need ____________
5. bikes need energy from __________
batteries, diesel, people, water, electricity.
-we can also classify machines by their function:
* thermal machines: make things hot or cold. Eg: air conditioners, heaters.
*information-processing machines: are used to communicate and to make calculations. Eg: computers, mobile phones and digital cameras.
* mechanical machines: produce movement,also known as kinetic energy. Eg: cars, motorcycles, electric toothbrushes and hairdryers.
http://www.learninggamesforkids.com/simple-machines-games.HTML
a lever:
https://youtu.be/9yZmOMY8qgw
SIMPLE MACHINES:
Inclined plane: ramp,slide, stairs.
wedge: ax, chisel, pushpin.
pulley: flagpole, crane, miniblind.
lever: hammer, pliers, scissors, seesaw,bottleopener.
screw: screw, corkscrew, jarlid.
Wheel and axe: skateboard, bicycle, pencil sharpener, doorknob.
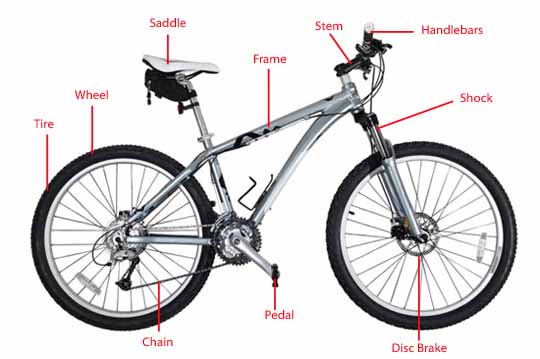
BICYCLE
What's so good about bicycles?
What's so good is that they get you places quickly without gobbling up fossil fuels like gasoline, diesel, and coal or creating pollution. They do that because they very efficiently convert the power our bodies produce into kinetic energy (energy of movement).If you're going uphill, you need to work against the force of gravity. If you're going fast, you're working against the force of air resistance (drag) pushing against your body. Sometimes there are bumps in the road.
CIRCUIT
An electric circuit is like a pathway made of wires that electrons can flow through. A battery or other power source gives the force (voltage) that makes the electrons move. When the electrons get to a device like a light bulb, your computer, or a refrigerator, they give it the power to make it work.
The word “circuit” sounds like “circle,” and a circuit needs to be circular to work
HOW A BIKE WORKS:
https://youtu.be/oZAc5t2lkvo
CIRCUITS
http://discoverykids.com/articles/how-do-electric-circuits-work/
https://youtu.be/VnnpLaKsqGU
ELECTROMAGNETISM
https://youtu.be/_ygmHnjNYNo
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is induced by the flow of an electric current through a coil of wire. The magnetic field disappears when the flow of electricity is stopped.
Electromagnets have at least two advantages over permanent magnets:
- the magnetic field can be switched on and off, or reversed, or its strength varied, by controlling the electric current, and
- they can generate a stronger magnetic field than a permanent magnet of similar size and weight.